DOCUMENTS
Documents required
Form 24, 49
M & A / Partnership Agreement
Insurance Policy(ies)
Information required
No. of directors / partners
Corporate Structure
Insurance Policy(ies)
Expected Growth of Company
Current Estimated Value of Company
CONSIDERATIONS
.Need for Buy Sell
Preliminary Assessment
Getting Help from Solicitor
What is a Buy Sell
Do I need a Buy Sell?
Explaining intricacies
Partnership / Entity Review
Establishing Funding Vehicle
Insurance Review
Tax Review
Crafting a Buy Sell
Drafting a Buy Sell Agreement
Components of Buy Sell
Type of Buy Sell
Agreed Purchase Price
Restrictions on Transfer
Funding Vehicle(s)
Triggering Event(s)
Valuation Method
Preparing for Contingencies
Margin of Financing
Monthly Installments
Execution of Buy Sell Agreement
Parties sign
Com Sec informed
Share certificates endorsed
Trigerring Event
Trigger initiates Buy Sell
Settlement of Purchase Price
Com Sec instructed to transfer
Transfer complete
Post Execution
Company Valuation
Purchase Price
Funding vehicle review
Insurance and Cash Reserves
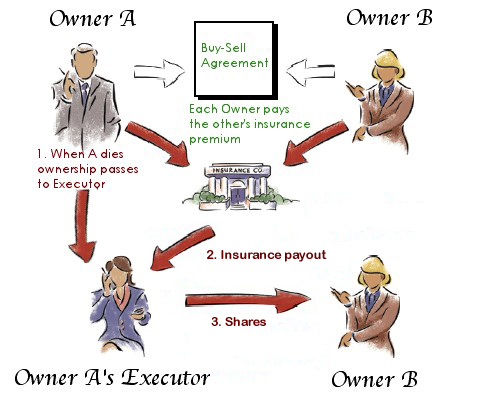
WHAT IS A BUY SELL?
|
AN AGREEMENT BETWEEN THE OWNERS OF A BUSINESS |
Legal Contract |
|
FOR PURCHASE OF EACH OTHERS INTEREST IN THE BUSINESS |
Restriction on Right to Transfer (compelling parties to buy and/or sell) |
|
WHICH PURCHASE IS TRIGGERED IN THE EVENT OF THE OWNER’S DEATH, DISABILITY, RETIREMENT, WITHDRAWAL FROM THE BUSINESS OR OTHER. |
Triggering Event |
WILL VS. BUY-SELL
– A Buy-Sell is used in addition to and
complements a will
– A Buy-Sell Agreement binds the successors and heirs of the owner – therefore,
a Buy-Sell Agreement overrides the Will
– Note however, to avoid complications, a Will should not be drafted to
contradict the provisions of Buy-Sell
TYPES OF BUY-SELL
– Entity Purchase (not
advisable for Malaysian companies)
– Cross Purchase
– Trusteed
COMPONENTS OF BUY-SELL
4 major components
– Buy-Sell Agreement
– Business Valuation
– Funding Vehicle
– Tax Implications Analysis
I. BUY SELL AGREEMENT
A. Triggering Event(s)
Insurable triggering events:
– Death
– Disability
Non-insurable triggering events:
– Retirement
– Attempt to Dissolve the Entity
– Irresolvable conflict among / between owners
– Owner’s desire to sell his interest
– Others
II. BUSINESS VALUATION
– Parties should agree on a fair method to
determine the sale price after the owner’s death can be problematic
– To forestall complications, it is better for co-owners of the business to
agree in advance of an owner’s death how interests in the business are to be valued
– Important if surviving owners wish to ensure that outgoing owner or his estate
is properly remunerated
– Methods include:
o Fair Market Value
o Cost
o Earnings-based valuation
o Financial statement derived valuation
o Agreement between parties
– Fair Market Value can be determined in 2 ways:
o To be agreed upon between owners at a specific time
each year; or
o The value is agreed to be equal to the amount of
insurance that has been purchased on the life of the owner.
o Or a combination of both the above.
III. FUNDING VEHICLE
– Alternative Funding Vehicles:
o Cash Flow generated by business
o Asset Sale
o Loan – borrowing the money
o Establish a Sinking Fund
o Reserves; or
o LIFE INSURANCE
– All but ONE OF THE ABOVE has serious disadvantages with respect to TIMING,
COST AND IMPACT on the business
– Funding mechanism ensures that money is available to carry out the agreement
when a triggering event occurs, without causing financial hardship to parties
involved
– The most carefully drafted Buy-Sell may prove useless if there are no funds to
purchase the deceased owner’s interest
– Life and Disability Insurance are THE ONLY RATIONALE SOLUTIONS
– Advantages of Life and Disability Insurance
o Insurance creates immediate funding in the event of
death or disability i.e. funds will be available when needed for the purchase
(As of 1 Nov 1991, claim arising from death can be submitted upon death)
o Death and disability benefit proceeds is income
tax-free
o Annual cost of life insurance is usually 1% - 4% of
the death benefit
o Premium paid is to a certain extent tax deductible
Income Tax Act
o Cash values are tax-exempt
o Cash values are readily accessible
o Malaysia does not have capital gains tax - increase
in value of business upon sale is not taxable. Therefore, estate of deceased
owner is not taxed on the price paid for the shares / ownership
IV. TAX IMPLICATIONS
– Premiums paid by the company vs. premiums paid by individuals (ie. partners in a cross-purchase)
CLASSES OF PEOPLE WHO HAVE NEED FOR BUY-SELL
– EVERY BUSINESS WITH MORE THAN ONE OWNER
– Any owner of closely-held business
– Family-owned business
WHAT HAPPENS TO A BUSINESS WITHOUT A BUY-SELL?
When the Owner dies,
– SOLE PROPRIETOR
o Unincorporated one-man business ceases to exist
– PARTNERSHIP
o Under section 35(1) of the Partnership Act 1961,
business instantly and automatically dissolved / ceases to exist
BENEFITS OF BUY-SELL
– To Deceased Estate:
o Provides Purchaser
o Generates Liquidity
o Avoidance of Dividend
– To Surviving Owner(s) / Purchaser:
o Reduces Friction between Heirs and Surviving
Shareholder
o Prevents Fights for Control between Surviving
Shareholders
o Prevents heirs from selling business at fire sale
o Provides Business Continuity and Family Security
o Provide for the predictable, transparent, and orderly
transfer of ownership
o Prevents Hostile Third Party Shareholders
o Provides for Funding
– To All Parties and Entity:
o Predictability and Continuity of Ownership
o Orderly Transfer of Ownership
o Provides a guaranteed buyer for your ownership
interest / Provides a marketplace for closely held business
o Establish a Fair Price for the Ownership Interest
o Protection of Majority and Minority Owners
CONFLICTING GOALS OF BENEFICIARIES
– Spouse may want continuing income
(profit distribution, dividends)
– Children involved in business may want growth (reinvestment of profits rather
than paying dividends)
– Children not involved in business may want cash (dividends, distribution or
liquidation)
– Employees want job security
– Other owners may not want former owner’s family to remain owners
– Beneficiaries may be:
o forced to work with and share control of the company
with an inexperienced or untrustworthy stranger who buys the interest of a
departing co-owner.
o forced to work with the spouse or other family member
of a deceased. There is always the substantial possibility that the family
member would be inexperienced, bitter, immature or air-headed.
o forced to co-own the company with a bankruptcy
trustee or creditor if a co-owner is forced to file for personal bankruptcy or
defaults on a personal loan secured by his ownership that no outsider wants to
buy and for which no insider will give you a decent price.
o surviving co-owners may argue with a departing
co-owner or her inheritors over what price should be paid for the interest that
is changing hands, resulting in an angry deadlock that spills over into business
operations.
Disclaimer :
Information and hyperlinks contained in http://www.liewchambers.com are for client reference only, and shall not be regarded as legal advice. Take note that the Liew Chambers does not guarantee the accuracy or reliability of such information, and disclaim all liability resulting from any reliance thereupon. Liew Chambers also does not endorse any information contained in or view expressed in any other webpage linked to our website. Applicable is our disclaimer statement.